PART THREE
If you happened to land on this page and missed
PART ONE, and
PART TWO, I would advise you go back and read those sections first.
This is what you'll find in
partone:
- Downloading and setting up the Android SDK
- Downloading the Processing IDE
- Setting up and preparing the Android device
- Running through a couple of Processing/Android sketches on an Andoid phone.
This is what you will find in
part two:
- Introducing Toasts (display messages)
- Looking out for BluetoothDevices using BroadcastReceivers
- Getting useful information from a discovered Bluetooth device
- Connecting to a Bluetooth Device
- An Arduino Bluetooth Sketch that can be used in this tutorial
 InputStream and OutputStream
InputStream and OutputStreamWe will now borrow some code from the
Android developers site to help us to establish communication between the Android phone and the Bluetooth shield on the Arduino. By this stage we have already scanned and discovered the bluetooth device and made a successful connection. We now need to create an
InputStream and
OutputStream to handle the flow of communication between the devices. Let us start with the Android/Processing Side.
The Android Developers site suggests to create a new Thread to handle the incoming and outgoing bytes, because this task uses "blocking" calls. Blocking calls means that the application will appear to be frozen until the call completes. We will create a new Thread to receive bytes through the BluetoothSocket's InputStream, and will send bytes to the Arduino through the BluetoothSocket's
OutputStream.
This Thread will continue to listen/send bytes for as long as needed, and will eventually close when we tell it to. We will also need a
Handler() to act on any bytes received via the
InputStream. The Handler is necessary to transfer information from the IO Thread to the main application thread. This is done by using a
Message class. Here is a summary of relevant code that we will subsequently add to the ConnectBluetooth sketch (which was described in
Part Two of this tutorial):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88 | import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
// Message types used by the Handler
public static final int MESSAGE_WRITE = 1;
public static final int MESSAGE_READ = 2;
// The Handler that gets information back from the Socket
private final Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_WRITE:
//Do something when writing
break;
case MESSAGE_READ:
//Get the bytes from the msg.obj
byte[] readBuf = (byte[]) msg.obj;
// construct a string from the valid bytes in the buffer
String readMessage = new String(readBuf, 0, msg.arg1);
break;
}
}
};
private class SendReceiveBytes implements Runnable {
private BluetoothSocket btSocket;
private InputStream btInputStream = null;
private OutputStream btOutputStream = null;
String TAG = "SendReceiveBytes";
public SendReceiveBytes(BluetoothSocket socket) {
btSocket = socket;
try {
btInputStream = btSocket.getInputStream();
btOutputStream = btSocket.getOutputStream();
}
catch (IOException streamError) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when getting input or output Stream");
}
}
public void run() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // buffer store for the stream
int bytes; // bytes returned from read()
// Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs
while (true) {
try {
// Read from the InputStream
bytes = btInputStream.read(buffer);
// Send the obtained bytes to the UI activity
mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_READ, bytes, -1, buffer)
.sendToTarget();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reading from btInputStream");
break;
}
}
}
/* Call this from the main activity to send data to the remote device */
public void write(byte[] bytes) {
try {
btOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when writing to btOutputStream");
}
}
/* Call this from the main activity to shutdown the connection */
public void cancel() {
try {
btSocket.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when closing the btSocket");
}
}
} |
Notice that we place an endless loop in the run() method to continuously read bytes from the InputStream. This continuous process of reading bytes needs to be a different thread from the main application otherwise it would cause the program to "hang". This thread passes any read bytes to the main application by using the Handler's .sendToTarget() method.
You will also notice the use of Log.e(TAG, ".....") commands. This is useful for debugging Android problems, especially when you comae across errors that generate a "caused the application to close unexpectedly" dialog box to appear on your phone. I personally created a shortcut of the adb.exe on my desktop and changed the target to
- "c:\[INSERT FOLDER]\Android\android-sdk\platform-tools\adb.exe" logcat *:E
The adb.exe program comes with the Android-SDK downloaded in
Part One . Once you find the adb.exe on your hard-drive, you just create a shortcut on your desktop. Right-click the shortcut, choose "Properties" and as indicated above, you change the last bit of the
Target to
So if you get an unexpected error on your android device, just go back to your laptop, and double-click on your new desktop adb.exe shortcut to get a better idea of where your program has gone wrong.
We will now incorporate the sketch above into our ConnectBluetooth Android/Processing App, however we will call this updated version "SendReceiveBytes"
Once we have created a successful connection, and created our Input/OutputStreams, we will send a single letter "r" to the Arduino via bluetooth, and if all goes well, we should see the light on the RGB Chainable LED turn Red (see further down for Arduino sketch).
I borrowed Byron's code snippet from
this site: to convert a string ("r") to a byte array, which is used in the write() method. The relevant code can be found on lines 199-208 below. I have bolded the lines numbers to make it a little easier to see the changes I made (compared to the previous sketch).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328 | /* SendReceiveBytes: Written by ScottC on 25 March 2013 using
Processing version 2.0b8
Tested on a Samsung Galaxy SII, with Android version 2.3.4
Android ADK - API 10 SDK platform */
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothServerSocket;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
public BluetoothSocket scSocket;
boolean foundDevice=false; //When true, the screen turns green.
boolean BTisConnected=false; //When true, the screen turns purple.
String serverName = "ArduinoBasicsServer";
// Message types used by the Handler
public static final int MESSAGE_WRITE = 1;
public static final int MESSAGE_READ = 2;
String readMessage="";
//Get the default Bluetooth adapter
BluetoothAdapter bluetooth = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
/*The startActivityForResult() within setup() launches an
Activity which is used to request the user to turn Bluetooth on.
The following onActivityResult() method is called when this
Activity exits. */
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
if (requestCode==0) {
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
ToastMaster("Bluetooth has been switched ON");
}
else {
ToastMaster("You need to turn Bluetooth ON !!!");
}
}
}
/* Create a BroadcastReceiver that will later be used to
receive the names of Bluetooth devices in range. */
BroadcastReceiver myDiscoverer = new myOwnBroadcastReceiver();
/* Create a BroadcastReceiver that will later be used to
identify if the Bluetooth device is connected */
BroadcastReceiver checkIsConnected = new myOwnBroadcastReceiver();
// The Handler that gets information back from the Socket
private final Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_WRITE:
//Do something when writing
break;
case MESSAGE_READ:
//Get the bytes from the msg.obj
byte[] readBuf = (byte[]) msg.obj;
// construct a string from the valid bytes in the buffer
readMessage = new String(readBuf, 0, msg.arg1);
break;
}
}
};
void setup() {
orientation(LANDSCAPE);
/*IF Bluetooth is NOT enabled, then ask user permission to enable it */
if (!bluetooth.isEnabled()) {
Intent requestBluetooth = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(requestBluetooth, 0);
}
/*If Bluetooth is now enabled, then register a broadcastReceiver to report any
discovered Bluetooth devices, and then start discovering */
if (bluetooth.isEnabled()) {
registerReceiver(myDiscoverer, new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND));
registerReceiver(checkIsConnected, new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_ACL_CONNECTED));
//Start bluetooth discovery if it is not doing so already
if (!bluetooth.isDiscovering()) {
bluetooth.startDiscovery();
}
}
}
void draw() {
//Display a green screen if a device has been found,
//Display a purple screen when a connection is made to the device
if (foundDevice) {
if (BTisConnected) {
background(170, 50, 255); // purple screen
}
else {
background(10, 255, 10); // green screen
}
}
//Display anything received from Arduino
text(readMessage, 10, 10);
}
/* This BroadcastReceiver will display discovered Bluetooth devices */
public class myOwnBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
ConnectToBluetooth connectBT;
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action=intent.getAction();
ToastMaster("ACTION:" + action);
//Notification that BluetoothDevice is FOUND
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
//Display the name of the discovered device
String discoveredDeviceName = intent.getStringExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_NAME);
ToastMaster("Discovered: " + discoveredDeviceName);
//Display more information about the discovered device
BluetoothDevice discoveredDevice = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
ToastMaster("getAddress() = " + discoveredDevice.getAddress());
ToastMaster("getName() = " + discoveredDevice.getName());
int bondyState=discoveredDevice.getBondState();
ToastMaster("getBondState() = " + bondyState);
String mybondState;
switch(bondyState) {
case 10:
mybondState="BOND_NONE";
break;
case 11:
mybondState="BOND_BONDING";
break;
case 12:
mybondState="BOND_BONDED";
break;
default:
mybondState="INVALID BOND STATE";
break;
}
ToastMaster("getBondState() = " + mybondState);
//Change foundDevice to true which will make the screen turn green
foundDevice=true;
//Connect to the discovered bluetooth device (SeeedBTSlave)
if (discoveredDeviceName.equals("SeeedBTSlave")) {
ToastMaster("Connecting you Now !!");
unregisterReceiver(myDiscoverer);
connectBT = new ConnectToBluetooth(discoveredDevice);
//Connect to the the device in a new thread
new Thread(connectBT).start();
}
}
//Notification if bluetooth device is connected
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_ACL_CONNECTED.equals(action)) {
ToastMaster("CONNECTED _ YAY");
while (scSocket==null) {
//do nothing
}
ToastMaster("scSocket" + scSocket);
BTisConnected=true; //turn screen purple
if (scSocket!=null) {
SendReceiveBytes sendReceiveBT = new SendReceiveBytes(scSocket);
new Thread(sendReceiveBT).start();
String red = "r";
byte[] myByte = stringToBytesUTFCustom(red);
sendReceiveBT.write(myByte);
}
}
}
}
public static byte[] stringToBytesUTFCustom(String str) {
char[] buffer = str.toCharArray();
byte[] b = new byte[buffer.length << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) {
int bpos = i << 1;
b[bpos] = (byte) ((buffer[i]&0xFF00)>>8);
b[bpos + 1] = (byte) (buffer[i]&0x00FF);
}
return b;
}
public class ConnectToBluetooth implements Runnable {
private BluetoothDevice btShield;
private BluetoothSocket mySocket = null;
private UUID uuid = UUID.fromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
public ConnectToBluetooth(BluetoothDevice bluetoothShield) {
btShield = bluetoothShield;
try {
mySocket = btShield.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(uuid);
}
catch(IOException createSocketException) {
//Problem with creating a socket
Log.e("ConnectToBluetooth", "Error with Socket");
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
/* Cancel discovery on Bluetooth Adapter to prevent slow connection */
bluetooth.cancelDiscovery();
try {
/*Connect to the bluetoothShield through the Socket. This will block
until it succeeds or throws an IOException */
mySocket.connect();
scSocket=mySocket;
}
catch (IOException connectException) {
Log.e("ConnectToBluetooth", "Error with Socket Connection");
try {
mySocket.close(); //try to close the socket
}
catch(IOException closeException) {
}
return;
}
}
/* Will cancel an in-progress connection, and close the socket */
public void cancel() {
try {
mySocket.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
private class SendReceiveBytes implements Runnable {
private BluetoothSocket btSocket;
private InputStream btInputStream = null;
private OutputStream btOutputStream = null;
String TAG = "SendReceiveBytes";
public SendReceiveBytes(BluetoothSocket socket) {
btSocket = socket;
try {
btInputStream = btSocket.getInputStream();
btOutputStream = btSocket.getOutputStream();
}
catch (IOException streamError) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when getting input or output Stream");
}
}
public void run() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // buffer store for the stream
int bytes; // bytes returned from read()
// Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs
while (true) {
try {
// Read from the InputStream
bytes = btInputStream.read(buffer);
// Send the obtained bytes to the UI activity
mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_READ, bytes, -1, buffer)
.sendToTarget();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reading from btInputStream");
break;
}
}
}
/* Call this from the main activity to send data to the remote device */
public void write(byte[] bytes) {
try {
btOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when writing to btOutputStream");
}
}
/* Call this from the main activity to shutdown the connection */
public void cancel() {
try {
btSocket.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when closing the btSocket");
}
}
}
/* My ToastMaster function to display a messageBox on the screen */
void ToastMaster(String textToDisplay) {
Toast myMessage = Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
textToDisplay,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
myMessage.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER, 0, 0);
myMessage.show();
} |
We will borrow the Arduino Sketch from my previous blog post (
here). Which should change the RGB LED to red when it receives an "r" through the bluetooth serial port.
You should also be able to send text to the Android phone by opening up the Serial Monitor on the Arduino IDE (although found this to be somewhat unreliable/unpredictable. I may need to investigate a better way of doing this, but it should work to some capacity (I sometimes find that a couple of letters go missing on transmision).
In this sketch I am using a
Bluetooth shield like this one, and have connected a
Grove Chainable RGB LED to it using a
Grove Universal 4 Pin Cable.
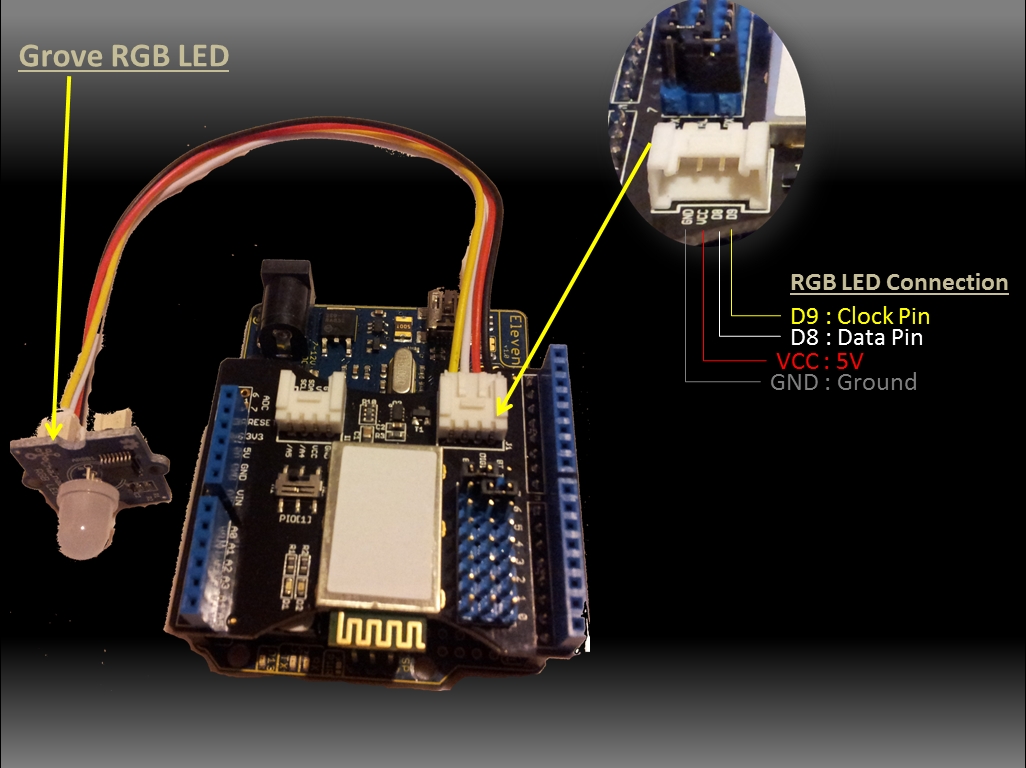 Arduino Sketch 2: Bluetooth RGB Colour Changer
Arduino Sketch 2: Bluetooth RGB Colour Changer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149 | /* This project combines the code from a few different sources.
This project was put together by ScottC on the 15/01/2013
http://arduinobasics.blogspot.com/
Bluetooth slave code by Steve Chang - downloaded from :
http://www.seeedstudio.com/wiki/index.php?title=Bluetooth_Shield
Grove Chainable RGB code can be found here :
http://www.seeedstudio.com/wiki/Grove_-_Chainable_RGB_LED#Introduction
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> //Software Serial Port
#define uint8 unsigned char
#define uint16 unsigned int
#define uint32 unsigned long int
#define RxD 6 // This is the pin that the Bluetooth (BT_TX) will transmit to the Arduino (RxD)
#define TxD 7 // This is the pin that the Bluetooth (BT_RX) will receive from the Arduino (TxD)
#define DEBUG_ENABLED 1
int Clkpin = 9; //RGB LED Clock Pin (Digital 9)
int Datapin = 8; //RGB LED Data Pin (Digital 8)
SoftwareSerial blueToothSerial(RxD,TxD);
/*----------------------SETUP----------------------------*/ void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Allow Serial communication via USB cable to computer (if required)
pinMode(RxD, INPUT); // Setup the Arduino to receive INPUT from the bluetooth shield on Digital Pin 6
pinMode(TxD, OUTPUT); // Setup the Arduino to send data (OUTPUT) to the bluetooth shield on Digital Pin 7
pinMode(13,OUTPUT); // Use onboard LED if required.
setupBlueToothConnection(); //Used to initialise the Bluetooth shield
pinMode(Datapin, OUTPUT); // Setup the RGB LED Data Pin
pinMode(Clkpin, OUTPUT); // Setup the RGB LED Clock pin
}
/*----------------------LOOP----------------------------*/ void loop() {
digitalWrite(13,LOW); //Turn off the onboard Arduino LED
char recvChar;
while(1){
if(blueToothSerial.available()){//check if there's any data sent from the remote bluetooth shield
recvChar = blueToothSerial.read();
Serial.print(recvChar); // Print the character received to the Serial Monitor (if required)
//If the character received = 'r' , then change the RGB led to display a RED colour
if(recvChar=='r'){
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(255, 0, 0); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
//If the character received = 'g' , then change the RGB led to display a GREEN colour
if(recvChar=='g'){
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(0, 255, 0); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
//If the character received = 'b' , then change the RGB led to display a BLUE colour
if(recvChar=='b'){
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(0, 0, 255); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
}
//You can use the following code to deal with any information coming from the Computer (serial monitor)
if(Serial.available()){
recvChar = Serial.read();
//This will send value obtained (recvChar) to the phone. The value will be displayed on the phone.
blueToothSerial.print(recvChar);
}
}
}
//The following code is necessary to setup the bluetooth shield ------copy and paste----------------
void setupBlueToothConnection()
{
blueToothSerial.begin(38400); //Set BluetoothBee BaudRate to default baud rate 38400
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STWMOD=0\r\n"); //set the bluetooth work in slave mode
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STNA=SeeedBTSlave\r\n"); //set the bluetooth name as "SeeedBTSlave"
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STOAUT=1\r\n"); // Permit Paired device to connect me
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STAUTO=0\r\n"); // Auto-connection should be forbidden here
delay(2000); // This delay is required.
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+INQ=1\r\n"); //make the slave bluetooth inquirable
Serial.println("The slave bluetooth is inquirable!");
delay(2000); // This delay is required.
blueToothSerial.flush();
}
//The following code snippets are used update the colour of the RGB LED-----copy and paste------------
void ClkProduce(void){
digitalWrite(Clkpin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(20);
digitalWrite(Clkpin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(20);
}
void Send32Zero(void){
unsigned char i;
for (i=0; i<32; i++){
digitalWrite(Datapin, LOW);
ClkProduce();
}
}
uint8 TakeAntiCode(uint8 dat){
uint8 tmp = 0;
if ((dat & 0x80) == 0){
tmp |= 0x02;
}
if ((dat & 0x40) == 0){
tmp |= 0x01;
}
return tmp;
}
// gray data
void DatSend(uint32 dx){
uint8 i;
for (i=0; i<32; i++){
if ((dx & 0x80000000) != 0){
digitalWrite(Datapin, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(Datapin, LOW);
}
dx <<= 1;
ClkProduce();
}
}
// data processing
void DataDealWithAndSend(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b){
uint32 dx = 0;
dx |= (uint32)0x03 << 30; // highest two bits 1,flag bits
dx |= (uint32)TakeAntiCode(b) << 28;
dx |= (uint32)TakeAntiCode(g) << 26;
dx |= (uint32)TakeAntiCode(r) << 24;
dx |= (uint32)b << 16;
dx |= (uint32)g << 8;
dx |= r;
DatSend(dx);
} |
 Some GUI Buttons
Some GUI ButtonsMy aim is to somewhat recreate the experience from a similar project I blogged about (
here). However I wanted to have much more control over the GUI. I will start by creating a few buttons, but will later look at making a much more fun/interactive design (hopefully). The following simple Android/Processing sketch will be totally independant of the sketch above, it will be a simple App that will have a few buttons which will change the colour of the background on the phone. Once we get the hang of this, we will incorporate it into our Bluetooth Sketch.
To start off with, we will need to download an Android/Processing library which will allow us to create the buttons that we will use in our App.
Unzip the apwidgets_r44.zip file and put the apwidgets folder into your default Processing sketch "libraries" folder. For more information about installing contributed libraries into you Processing IDE - have a look at
this site.
You will need to reboot your Processing IDE before being able to see the "apwidgets" item appear in the Processing IDE's menu,
- Sketch > Import Library : Under the "Contributed" list item.
If you cannot see this menu item, then you will need to try again. Make sure you are putting it into the default sketch libraries folder, which may not be in the same folder as the processing IDE. To find out the default sketch location - look here:
- File > Preferences > Sketchbook location
Ok, now that you have the APWidgets library installed in your Processing IDE, make sure you are still in Andorid Mode, and copy the following sketch into the IDE, and run the program on your device. This sketch borrows heavily from the APWidgets Button example, which can be found
here.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55 | import apwidgets.*;
APWidgetContainer widgetContainer;
APButton redButton, greenButton, blueButton, offButton;
String buttonText="";
int buttonWidth=0;
int buttonHeight=0;
int n=4; //number of buttons
int gap=10; //gap between buttons
void setup() {
buttonWidth=((width/n)-(n*gap));
buttonHeight=(height/2);
widgetContainer = new APWidgetContainer(this); //create new container for widgets
redButton =new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-4)+(gap*1)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "RED"); //Create a RED button
greenButton = new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-3)+(gap*2)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "GREEN"); //Create a GREEN button
blueButton = new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-2)+(gap*3)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "BLUE"); //Create a BLUE button
offButton = new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-1)+(gap*4)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "OFF"); //Create a OFF button
widgetContainer.addWidget(redButton); //place red button in container
widgetContainer.addWidget(greenButton); //place green button in container
widgetContainer.addWidget(blueButton);//place blue button in container
widgetContainer.addWidget(offButton);//place off button in container
background(0); //Start with a black background
}
void draw() {
//Change the text based on the button being pressed.
text(buttonText, 10, buttonHeight+(buttonHeight/2));
}
//onClickWidget is called when a widget is clicked/touched
void onClickWidget(APWidget widget) {
if (widget == redButton) { //if the red button was clicked
buttonText="RED";
background(255, 0, 0);
}
else if (widget == greenButton) { //if the green button was clicked
buttonText="GREEN";
background(0, 255, 0);
}
else if (widget == blueButton) { //if the blue button was clicked
buttonText="BLUE";
background(0, 0, 255);
}
else if (widget == offButton) { //if the off button was clicked
buttonText="OFF";
background(0);
}
} |
The sketch creates 4 buttons, one for Red, Green, Blue and Off. In this example, we use the onClickWidget() method to deal with button_click events, which we use to change the colour of the background. I forgot to include the following line in the setup() method:
This will force the application to go into landscape mode, which is what I intended.
 Bluetooth Buttons : Adding Buttons to the Bluetooth project
Bluetooth Buttons : Adding Buttons to the Bluetooth projectWe will now incorporate the Buttons sketch into our Bluetooth project so that when we press a button, it will send a letter to the Arduino via Bluetooth. The letter will be used by the Arduino to decide what colour to display on the Chainable RGB LED. We will still keep the previous functionality of changing the LED to RED when a successful Input/OutputStream is created, because this will be the signal to suggest that it is now ok to press the buttons (and we should see it work).
Here is the updated Android/Processing sketch
Android/Processing Sketch 8: Bluetooth App1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404 | /* BluetoothApp1: Written by ScottC on 25 March 2013 using
Processing version 2.0b8
Tested on a Samsung Galaxy SII, with Android version 2.3.4
Android ADK - API 10 SDK platform
Apwidgets version: r44 */
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothServerSocket;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket;
import apwidgets.*;
public BluetoothSocket scSocket;
//Used for the GUI**************************************
APWidgetContainer widgetContainer;
APButton redButton, greenButton, blueButton, offButton;
String buttonText="";
int buttonWidth=0;
int buttonHeight=0;
int n=4; //number of buttons
int gap=10; //gap between buttons
boolean foundDevice=false; //When true, the screen turns green.
boolean BTisConnected=false; //When true, the screen turns purple.
String serverName = "ArduinoBasicsServer";
// Message types used by the Handler
public static final int MESSAGE_WRITE = 1;
public static final int MESSAGE_READ = 2;
String readMessage="";
//Used to send bytes to the Arduino
SendReceiveBytes sendReceiveBT=null;
//Get the default Bluetooth adapter
BluetoothAdapter bluetooth = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
/*The startActivityForResult() within setup() launches an
Activity which is used to request the user to turn Bluetooth on.
The following onActivityResult() method is called when this
Activity exits. */
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
if (requestCode==0) {
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
ToastMaster("Bluetooth has been switched ON");
}
else {
ToastMaster("You need to turn Bluetooth ON !!!");
}
}
}
/* Create a BroadcastReceiver that will later be used to
receive the names of Bluetooth devices in range. */
BroadcastReceiver myDiscoverer = new myOwnBroadcastReceiver();
/* Create a BroadcastReceiver that will later be used to
identify if the Bluetooth device is connected */
BroadcastReceiver checkIsConnected = new myOwnBroadcastReceiver();
// The Handler that gets information back from the Socket
private final Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_WRITE:
//Do something when writing
break;
case MESSAGE_READ:
//Get the bytes from the msg.obj
byte[] readBuf = (byte[]) msg.obj;
// construct a string from the valid bytes in the buffer
readMessage = new String(readBuf, 0, msg.arg1);
break;
}
}
};
void setup() {
orientation(LANDSCAPE);
//Setup GUI********************************
buttonWidth=((width/n)-(n*gap));
buttonHeight=(height/2);
widgetContainer = new APWidgetContainer(this); //create new container for widgets
redButton =new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-4)+(gap*1)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "RED"); //Create a RED button
greenButton = new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-3)+(gap*2)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "GREEN"); //Create a GREEN button
blueButton = new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-2)+(gap*3)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "BLUE"); //Create a BLUE button
offButton = new APButton((buttonWidth*(n-1)+(gap*4)), gap, buttonWidth, buttonHeight, "OFF"); //Create a OFF button
widgetContainer.addWidget(redButton); //place red button in container
widgetContainer.addWidget(greenButton); //place green button in container
widgetContainer.addWidget(blueButton);//place blue button in container
widgetContainer.addWidget(offButton);//place off button in container
background(0); //Start with a black background
/*IF Bluetooth is NOT enabled, then ask user permission to enable it */
if (!bluetooth.isEnabled()) {
Intent requestBluetooth = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(requestBluetooth, 0);
}
/*If Bluetooth is now enabled, then register a broadcastReceiver to report any
discovered Bluetooth devices, and then start discovering */
if (bluetooth.isEnabled()) {
registerReceiver(myDiscoverer, new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND));
registerReceiver(checkIsConnected, new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_ACL_CONNECTED));
//Start bluetooth discovery if it is not doing so already
if (!bluetooth.isDiscovering()) {
bluetooth.startDiscovery();
}
}
}
void draw() {
//Display a green screen if a device has been found,
//Display a purple screen when a connection is made to the device
if (foundDevice) {
if (BTisConnected) {
background(170, 50, 255); // purple screen
}
else {
background(10, 255, 10); // green screen
}
}
//Change the text based on the button being pressed.
text(buttonText, 10, buttonHeight+(buttonHeight/2));
//Display anything received from Arduino
text(readMessage, 10, buttonHeight+(buttonHeight/2)+30);
}
/* This BroadcastReceiver will display discovered Bluetooth devices */
public class myOwnBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
ConnectToBluetooth connectBT;
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action=intent.getAction();
ToastMaster("ACTION:" + action);
//Notification that BluetoothDevice is FOUND
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
//Display the name of the discovered device
String discoveredDeviceName = intent.getStringExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_NAME);
ToastMaster("Discovered: " + discoveredDeviceName);
//Display more information about the discovered device
BluetoothDevice discoveredDevice = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
ToastMaster("getAddress() = " + discoveredDevice.getAddress());
ToastMaster("getName() = " + discoveredDevice.getName());
int bondyState=discoveredDevice.getBondState();
ToastMaster("getBondState() = " + bondyState);
String mybondState;
switch(bondyState) {
case 10:
mybondState="BOND_NONE";
break;
case 11:
mybondState="BOND_BONDING";
break;
case 12:
mybondState="BOND_BONDED";
break;
default:
mybondState="INVALID BOND STATE";
break;
}
ToastMaster("getBondState() = " + mybondState);
//Change foundDevice to true which will make the screen turn green
foundDevice=true;
//Connect to the discovered bluetooth device (SeeedBTSlave)
if (discoveredDeviceName.equals("SeeedBTSlave")) {
ToastMaster("Connecting you Now !!");
unregisterReceiver(myDiscoverer);
connectBT = new ConnectToBluetooth(discoveredDevice);
//Connect to the the device in a new thread
new Thread(connectBT).start();
}
}
//Notification if bluetooth device is connected
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_ACL_CONNECTED.equals(action)) {
ToastMaster("CONNECTED _ YAY");
int counter=0;
while (scSocket==null) {
//do nothing
}
ToastMaster("scSocket" + scSocket);
BTisConnected=true; //turn screen purple
if (scSocket!=null) {
sendReceiveBT = new SendReceiveBytes(scSocket);
new Thread(sendReceiveBT).start();
String red = "r";
byte[] myByte = stringToBytesUTFCustom(red);
sendReceiveBT.write(myByte);
}
}
}
}
public static byte[] stringToBytesUTFCustom(String str) {
char[] buffer = str.toCharArray();
byte[] b = new byte[buffer.length << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) {
int bpos = i << 1;
b[bpos] = (byte) ((buffer[i]&0xFF00)>>8);
b[bpos + 1] = (byte) (buffer[i]&0x00FF);
}
return b;
}
public class ConnectToBluetooth implements Runnable {
private BluetoothDevice btShield;
private BluetoothSocket mySocket = null;
private UUID uuid = UUID.fromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
public ConnectToBluetooth(BluetoothDevice bluetoothShield) {
btShield = bluetoothShield;
try {
mySocket = btShield.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(uuid);
}
catch(IOException createSocketException) {
//Problem with creating a socket
Log.e("ConnectToBluetooth", "Error with Socket");
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
/* Cancel discovery on Bluetooth Adapter to prevent slow connection */
bluetooth.cancelDiscovery();
try {
/*Connect to the bluetoothShield through the Socket. This will block
until it succeeds or throws an IOException */
mySocket.connect();
scSocket=mySocket;
}
catch (IOException connectException) {
Log.e("ConnectToBluetooth", "Error with Socket Connection");
try {
mySocket.close(); //try to close the socket
}
catch(IOException closeException) {
}
return;
}
}
// Will allow you to get the socket from this class
public BluetoothSocket getSocket() {
return mySocket;
}
/* Will cancel an in-progress connection, and close the socket */
public void cancel() {
try {
mySocket.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
private class SendReceiveBytes implements Runnable {
private BluetoothSocket btSocket;
private InputStream btInputStream = null;
;
private OutputStream btOutputStream = null;
String TAG = "SendReceiveBytes";
public SendReceiveBytes(BluetoothSocket socket) {
btSocket = socket;
try {
btInputStream = btSocket.getInputStream();
btOutputStream = btSocket.getOutputStream();
}
catch (IOException streamError) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when getting input or output Stream");
}
}
public void run() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // buffer store for the stream
int bytes; // bytes returned from read()
// Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs
while (true) {
try {
// Read from the InputStream
bytes = btInputStream.read(buffer);
// Send the obtained bytes to the UI activity
mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_READ, bytes, -1, buffer)
.sendToTarget();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reading from btInputStream");
break;
}
}
}
/* Call this from the main activity to send data to the remote device */
public void write(byte[] bytes) {
try {
btOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when writing to btOutputStream");
}
}
/* Call this from the main activity to shutdown the connection */
public void cancel() {
try {
btSocket.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error when closing the btSocket");
}
}
}
/* My ToastMaster function to display a messageBox on the screen */
void ToastMaster(String textToDisplay) {
Toast myMessage = Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
textToDisplay,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
myMessage.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER, 0, 0);
myMessage.show();
}
//onClickWidget is called when a widget is clicked/touched
void onClickWidget(APWidget widget) {
String sendLetter = "";
//Disable the previous Background colour changers
foundDevice=false;
BTisConnected=false;
if (widget == redButton) { //if the red button was clicked
buttonText="RED";
background(255, 0, 0);
sendLetter = "r";
}
else if (widget == greenButton) { //if the green button was clicked
buttonText="GREEN";
background(0, 255, 0);
sendLetter = "g";
}
else if (widget == blueButton) { //if the blue button was clicked
buttonText="BLUE";
background(0, 0, 255);
sendLetter = "b";
}
else if (widget == offButton) { //if the off button was clicked
buttonText="OFF";
background(0);
sendLetter = "x";
}
byte[] myByte = stringToBytesUTFCustom(sendLetter);
sendReceiveBT.write(myByte);
} |
The sketch above has been thrown together without much planning or consideration for code efficiency. It was deliberately done this way so that you could see and follow the incremental approach used to create this Android/Processing Bluetooth App. I will do my best to rewrite and simplify some of the code, however, I don't anticipate the final sketch will be a short script.
You should have noticed that I included a fourth button called an "off" button. This will turn off the RGB led. However, the Arduino code in its current format does not know what to do with an 'x'. So we will update the sketch as follows:
Arduino Sketch 3: Bluetooth RGB Colour Changer (with OFF option) 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170 | /* This project combines the code from a few different sources.
This project was put together by ScottC on the 15/01/2013
http://arduinobasics.blogspot.com/
Bluetooth slave code by Steve Chang - downloaded from :
http://www.seeedstudio.com/wiki/index.php?title=Bluetooth_Shield
Grove Chainable RGB code can be found here :
http://www.seeedstudio.com/wiki/Grove_-_Chainable_RGB_LED#Introduction
Updated on 25 March 2013: Receive 'x' to turn off RGB LED.
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> //Software Serial Port
#define uint8 unsigned char
#define uint16 unsigned int
#define uint32 unsigned long int
#define RxD 6 // This is the pin that the Bluetooth (BT_TX) will transmit to the Arduino (RxD)
#define TxD 7 // This is the pin that the Bluetooth (BT_RX) will receive from the Arduino (TxD)
#define DEBUG_ENABLED 1
int Clkpin = 9; //RGB LED Clock Pin (Digital 9)
int Datapin = 8; //RGB LED Data Pin (Digital 8)
SoftwareSerial blueToothSerial(RxD, TxD);
/*----------------------SETUP----------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Allow Serial communication via USB cable to computer (if required)
pinMode(RxD, INPUT); // Setup the Arduino to receive INPUT from the bluetooth shield on Digital Pin 6
pinMode(TxD, OUTPUT); // Setup the Arduino to send data (OUTPUT) to the bluetooth shield on Digital Pin 7
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Use onboard LED if required.
setupBlueToothConnection(); //Used to initialise the Bluetooth shield
pinMode(Datapin, OUTPUT); // Setup the RGB LED Data Pin
pinMode(Clkpin, OUTPUT); // Setup the RGB LED Clock pin
}
/*----------------------LOOP----------------------------*/
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, LOW); //Turn off the onboard Arduino LED
char recvChar;
while (1) {
if (blueToothSerial.available()) {//check if there's any data sent from the remote bluetooth shield
recvChar = blueToothSerial.read();
Serial.print(recvChar); // Print the character received to the Serial Monitor (if required)
//If the character received = 'r' , then change the RGB led to display a RED colour
if (recvChar=='r') {
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(255, 0, 0); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
//If the character received = 'g' , then change the RGB led to display a GREEN colour
if (recvChar=='g') {
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(0, 255, 0); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
//If the character received = 'b' , then change the RGB led to display a BLUE colour
if (recvChar=='b') {
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(0, 0, 255); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
//If the character received = 'x' , then turn RGB led OFF
if (recvChar=='x') {
Send32Zero(); // begin
DataDealWithAndSend(0, 0, 0); // first node data
Send32Zero(); // send to update data
}
}
//You can use the following code to deal with any information coming from the Computer (serial monitor)
if (Serial.available()) {
recvChar = Serial.read();
//This will send value obtained (recvChar) to the phone. The value will be displayed on the phone.
blueToothSerial.print(recvChar);
}
}
}
//The following code is necessary to setup the bluetooth shield ------copy and paste----------------
void setupBlueToothConnection()
{
blueToothSerial.begin(38400); //Set BluetoothBee BaudRate to default baud rate 38400
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STWMOD=0\r\n"); //set the bluetooth work in slave mode
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STNA=SeeedBTSlave\r\n"); //set the bluetooth name as "SeeedBTSlave"
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STOAUT=1\r\n"); // Permit Paired device to connect me
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+STAUTO=0\r\n"); // Auto-connection should be forbidden here
delay(2000); // This delay is required.
blueToothSerial.print("\r\n+INQ=1\r\n"); //make the slave bluetooth inquirable
Serial.println("The slave bluetooth is inquirable!");
delay(2000); // This delay is required.
blueToothSerial.flush();
}
//The following code snippets are used update the colour of the RGB LED-----copy and paste------------
void ClkProduce(void) {
digitalWrite(Clkpin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(20);
digitalWrite(Clkpin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(20);
}
void Send32Zero(void) {
unsigned char i;
for (i=0; i<32; i++) {
digitalWrite(Datapin, LOW);
ClkProduce();
}
}
uint8 TakeAntiCode(uint8 dat) {
uint8 tmp = 0;
if ((dat & 0x80) == 0) {
tmp |= 0x02;
}
if ((dat & 0x40) == 0) {
tmp |= 0x01;
}
return tmp;
}
// gray data
void DatSend(uint32 dx) {
uint8 i;
for (i=0; i<32; i++) {
if ((dx & 0x80000000) != 0) {
digitalWrite(Datapin, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(Datapin, LOW);
}
dx <<= 1;
ClkProduce();
}
}
// data processing
void DataDealWithAndSend(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b) {
uint32 dx = 0;
dx |= (uint32)0x03 << 30; // highest two bits 1,flag bits
dx |= (uint32)TakeAntiCode(b) << 28;
dx |= (uint32)TakeAntiCode(g) << 26;
dx |= (uint32)TakeAntiCode(r) << 24;
dx |= (uint32)b << 16;
dx |= (uint32)g << 8;
dx |= r;
DatSend(dx);
} |
Well that concludes part 3.
Part 4 is a summary of the finished project with videos, screenshots, parts used etc.
I hope you found this tutorial useful. I would love to receive any advice on how I could improve these tutorials (please put your recommendations in comments below).
Reason for this Project:While there are quite a few people creating Android/Arduino projects, I have not been able to find many that show how these are being accomplished using the Android/Processing IDE, and even less on how they are using Bluetooth in their Android/Processing projects. I hope my piecing of information will spark some creative Bluetooth projects of your own.
Description:
Bluetooth Android Processing 3
Rating:
3.5
Reviewer:
Unknown
ItemReviewed:
Bluetooth Android Processing 3

 you are reading post about
you are reading post about 
0 comments:
Post a Comment